What Is Bitcoin (BTC)?
Bitcoin (BTC) is a decentralized digital currency created in 2009. It allows peer-to-peer transactions without the need for intermediaries.
Utilizing blockchain technology, Bitcoin offers a secure and transparent public ledger where all transactions are recorded and verified by a network of nodes.
This decentralization enhances security and reduces traditional banking reliance. Users store their Bitcoin in digital wallets, protected by cryptographic keys.
While Bitcoin presents benefits such as lower transaction fees and increased control over funds, it also poses risks, including market volatility and regulatory uncertainties.
Key Takeaways:
ShowHistory of Bitcoin
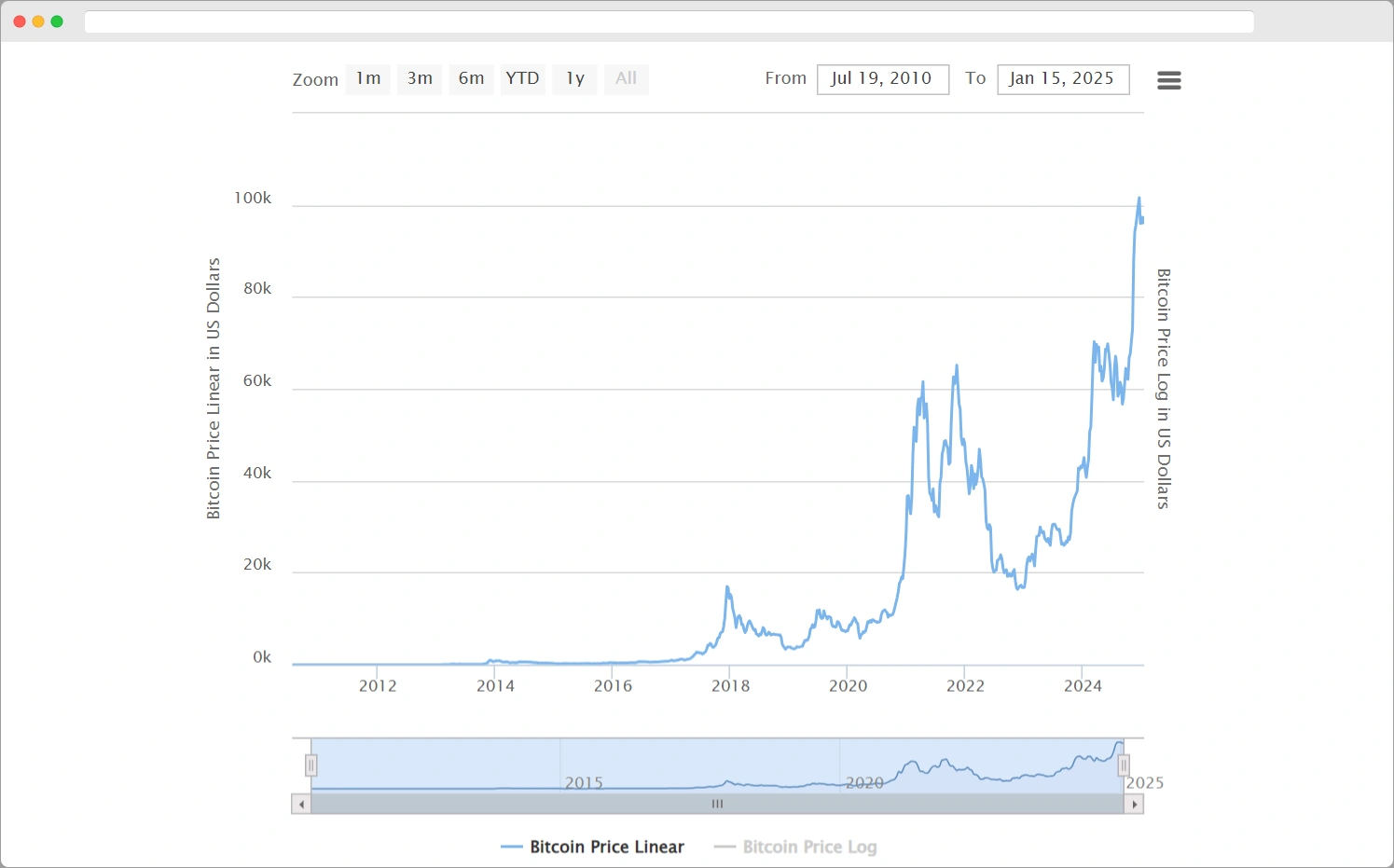
Although the concept of digital currency predates Bitcoin, the cryptocurrency was introduced in 2009 by an anonymous person or group under the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto.
The release of the Bitcoin whitepaper, titled “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System,” marked a pivotal moment in financial technology.
Nakamoto’s vision was to create a decentralized form of currency that operates without the need for intermediaries, thereby enhancing security and reducing fraud risks.
The first Bitcoin transaction took place in January 2009, when Nakamoto mined the genesis block.
Over the ensuing years, Bitcoin gained traction, attracting both individual users and institutional interest.
Its underlying technology, blockchain, provided a transparent and secure ledger, further solidifying Bitcoin’s position as a revolutionary financial instrument amidst growing global uncertainty.
How Bitcoin Works
To understand how Bitcoin works, it is essential to grasp the fundamental principles of blockchain technology and cryptographic security that underpin it.
Bitcoin operates on a decentralized network, where transactions are recorded on a public ledger called the blockchain.
Each transaction is verified by a network of nodes, guaranteeing integrity through consensus mechanisms.
This decentralized approach eliminates the need for intermediaries, enhancing security and reducing fraud risk.
Users store their Bitcoin in digital wallets, which utilize cryptographic keys to certify only authorized individuals can access their funds.
In addition, Bitcoin employs advanced encryption techniques, making it challenging for unauthorized parties to manipulate or counterfeit transactions.
This combination of decentralization and cryptography fosters a secure environment for users, promoting trust in the digital currency.
Blockchain Technology Explained
Blockchain technology serves as the backbone of Bitcoin and many other cryptocurrencies, revolutionizing how digital transactions are recorded and verified.
This decentralized ledger system enhances security and transparency, mitigating risks associated with traditional banking methods.
Each transaction is encrypted and linked to previous entries, creating an immutable chain that is nearly impossible to alter or counterfeit.
Key features of blockchain technology include:
- Decentralization: Eliminates single points of failure.
- Transparency: All transactions are publicly accessible.
- Security: Uses cryptographic techniques to safeguard data.
- Immutability: Once recorded, data cannot be changed without consensus.
- Consensus Mechanisms: Guarantees all participants agree on the validity of transactions.
These attributes contribute to a more reliable digital transaction environment, appealing to those prioritizing safety.
Benefits of Using Bitcoin

The advantages of utilizing Bitcoin extend beyond its underlying blockchain technology, offering users a range of benefits that enhance their financial transactions.
One significant benefit is enhanced security; Bitcoin employs cryptographic protocols that protect users from fraud and unauthorized access.
Additionally, Bitcoin transactions are decentralized, reducing reliance on traditional banking systems and their associated fees.
This decentralization also fosters greater privacy, allowing users to transact without disclosing personal information.
Moreover, Bitcoin’s borderless nature facilitates international transactions, eliminating currency conversion issues and delays.
Users also enjoy increased control over their funds, as Bitcoin transactions are irreversible, providing a safeguard against chargebacks.
Overall, these benefits contribute to a more secure and efficient financial ecosystem for users seeking safety in their transactions.
Risks and Challenges
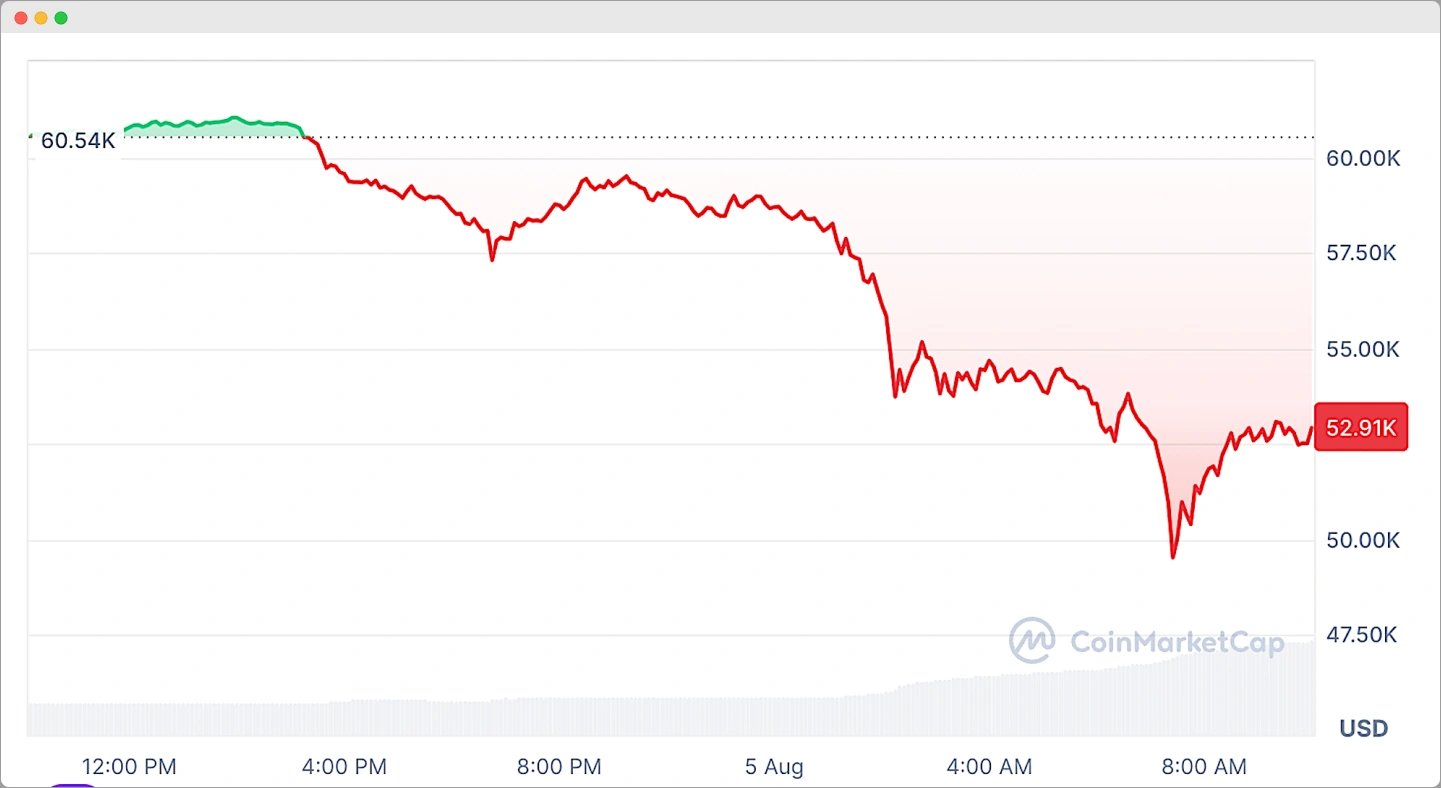
While Bitcoin presents numerous advantages, it is essential to weigh the risks and challenges associated with its use.
Security concerns, regulatory uncertainties, and market volatility can substantially impact users. Furthermore, the potential for loss due to hacking or fraud remains a critical issue.
Awareness of these challenges is essential for anyone considering Bitcoin as an investment or transactional tool.
- Market Volatility: Prices can fluctuate dramatically.
- Regulatory Risks: Governments may impose strict regulations or bans.
- Security Vulnerabilities: Digital wallets can be susceptible to hacking.
- Lack of Consumer Protections: Transactions are irreversible, with limited recourse.
- Environmental Concerns: High energy consumption associated with mining activities.
Wrapping Up
In the domain of digital finance, Bitcoin stands as a beacon of innovation, juxtaposed against traditional monetary systems.
While its decentralized nature offers unprecedented autonomy and security, the inherent volatility and regulatory uncertainties present significant challenges.
The ongoing evolution of blockchain technology further underscores this duality, revealing both the potential for transformative change and the risks of widespread adoption.
Ultimately, understanding Bitcoin necessitates a careful consideration of its benefits alongside its complexities, highlighting the intricate balance within this revolutionary asset.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How Can I Buy Bitcoin Safely?
To buy Bitcoin safely, utilize reputable exchanges with strong security measures. Enable two-factor authentication, store your assets in secure wallets, and remain vigilant against phishing attacks. Always conduct thorough research before making transactions.
What Are the Tax Implications of Bitcoin Transactions?
Traversing the tax implications of Bitcoin transactions can feel like traversing a complex labyrinth. Each transaction may incur capital gains tax, necessitating meticulous record-keeping to guarantee compliance and safeguard against potential financial pitfalls.
Can Bitcoin Be Used for Everyday Purchases?
Bitcoin can indeed be utilized for everyday purchases at various retailers that accept cryptocurrency. However, users should prioritize security and regulatory compliance, ensuring they understand the implications of using digital currencies in their transactions.
What Wallets Are Best for Storing Bitcoin?
When selecting wallets for Bitcoin storage, prioritize security features. Hardware wallets, such as Ledger and Trezor, offer robust protection, while reputable software wallets, like Exodus and Electrum, provide user-friendly interfaces with encryption capabilities for enhanced safety.
Is Bitcoin Legal in My Country?
Isn’t it prudent to ascertain the legality of an asset before engaging with it? Bitcoin’s legal status varies globally; consequently, consulting local regulations and seeking legal advice is essential to guarantee compliance and safeguard your investments.

